 Created in 2007 by the Pennsylvania Office of Child Development and Early Learning (OCDEL), The Pennsylvania Key implements the work and supports the policies developed and managed by OCDEL. Learn More. >
Created in 2007 by the Pennsylvania Office of Child Development and Early Learning (OCDEL), The Pennsylvania Key implements the work and supports the policies developed and managed by OCDEL. Learn More. >Experiencing excessive stress, poor nutrition, or toxic environmental exposures during pregnancy can affect fetal development, with long-lasting impacts into adulthood, such as increased risk for heart disease, obesity, diabetes, and mental health conditions.
Pregnancy-related deaths occur during pregnancy, delivery, and up to 1 year postpartum. Maternal Mortality Review Committees (2017–2019) determined that over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths were preventable. Four in 5 pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable _ CDC Archive.pdf
Underlying causes of pregnancy-related death include:
Access to maternal health services is critical to improving health outcomes for birthing people and infants. By ensuring that women get high-quality care during and after pregnancy, infants can get a healthy start to life. However, challenges such as maternal health deserts, hospital financial stability, and health care access disparities pose alarming risks to maternal health.
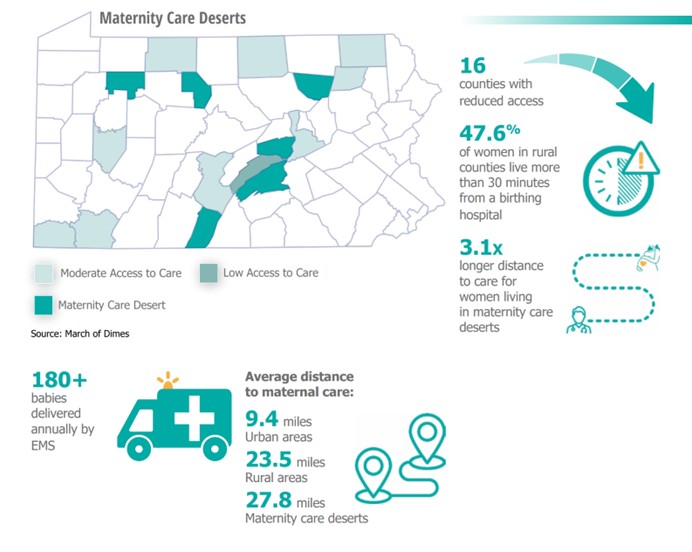
As more obstetric units close across Pennsylvania, maternity care deserts have increased. Since 2005, 38 Pennsylvania hospitals have had to close their labor and delivery units, 18 of them in rural communities. Nearly half of women in rural Pennsylvania communities live more than 30 minutes from a birthing hospital.
Help prevent pregnancy-related deaths
Be aware of urgent warning signs and symptoms during pregnancy and in the year after delivery. Signs and Symptoms of Urgent Maternal Warnings Signs | HEAR HER Campaign | CDC
Help support a healthy pregnancy
See March of Dimes: Help us improve the health of all moms and babies | March of Dimes
Get early, trusted, regular, and supportive prenatal care
Find supportive and trusted healthcare providers who provide emotional, physical, and informational support during pregnancy, delivery and after childbirth. Perinatal and Parenting Support | Department of Human Services | Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
Listen to the concerns of people who are pregnant and have been pregnant during the last year and help them get the care they need. See Pennsylvania’s Action Plan for Maternal Health: action-plan-for-maternal-health-final.pdf
Eat healthy
Eat a well-balanced diet and take prenatal vitamins.
Get Dental Care
It is safe and important to get dental care during pregnancy.
Prevent Infections
Avoid Harmful Toxins
Toxins include lead, gasses, solvents, pesticides, asbestos and other substances.
Prevent Lead Poisoning
Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Data From Maternal Mortality Review Committees in 36 U.S. States, 2017–2019: Four in 5 pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable _ CDC Archive.pdf
Journal of the American Medical Association JAMA Network Open. October 15, 2025. First-Trimester mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination and Risk of Major Congenital Anomalies. In this nationwide cohort study of 527,564 live-born infants, 130,338 (24.7%) were exposed to an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine during the first trimester of pregnancy. There was no association with an increased risk for 75 different major congenital malformations, whether examined overall, grouped by organ systems, or individually.
Disclaimer: This is the most updated information at release time. The information in Health Trends is not a Pennsylvania regulatory requirement for early childhood providers. Pennsylvania early childhood providers with regulatory requirements should contact their Cert rep or the Bureau of Certification.